Remote Bloodhound
GitHub Repo
Prerequisites
impacketldap3dnspython
Installation
python3 -m pip install bloodhoundUsage Example
Nmap LDAP Enumeration
Find the FQDN of the domain controller:
# Look for the dnsHostName attribute
sudo nmap -Pn -T4 -p 389,636 --script ldap-rootdse <domain-controller-ip> | grep dnsHostName | sort -u
# Post-compromise scan through a proxy
# Look for the dnsHostName attribute
sudo proxychains -q nmap -Pn -T4 -sT -p 389,636 --script ldap-rootdse <domain-controller-ip> | grep dnsHostName | sort -uAdd Hosts Entry
Add the FQDN of the domain controller to your /etc/hosts file:
echo '10.80.80.2 DC01.ad.lab' | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsRun Remote Bloodhound Script
# Display help output
bloodhound-python
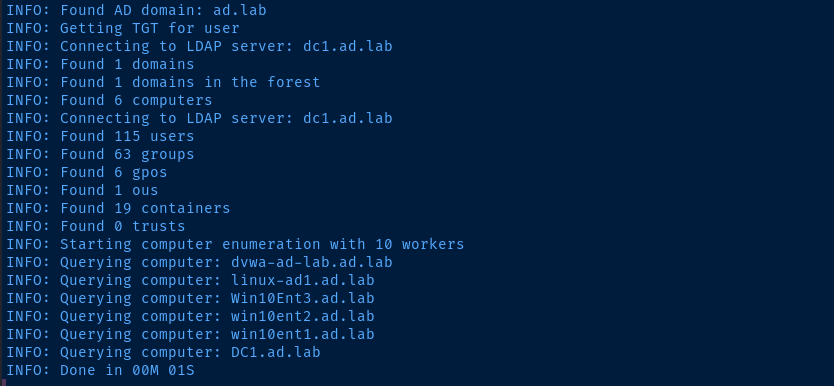
# Collect all information on the domain (requires credential)
# If LDAPS run with --use-ldaps
bloodhound-python -c All -u username -p password -d domain.tld -dc dc0.domain.tld -ns domain-controller-ip
# Collect all information on the domain via post-compromise proxy
# If LDAPS run with --use-ldaps
proxychains -q bloodhound-python -c All -u username -p password -d domain.tld -dc dc0.domain.tld -ns omain-controller-ip --dns-tcpProcess Collected Information
By default bloodhound-python will output a series of files in your current working directory:
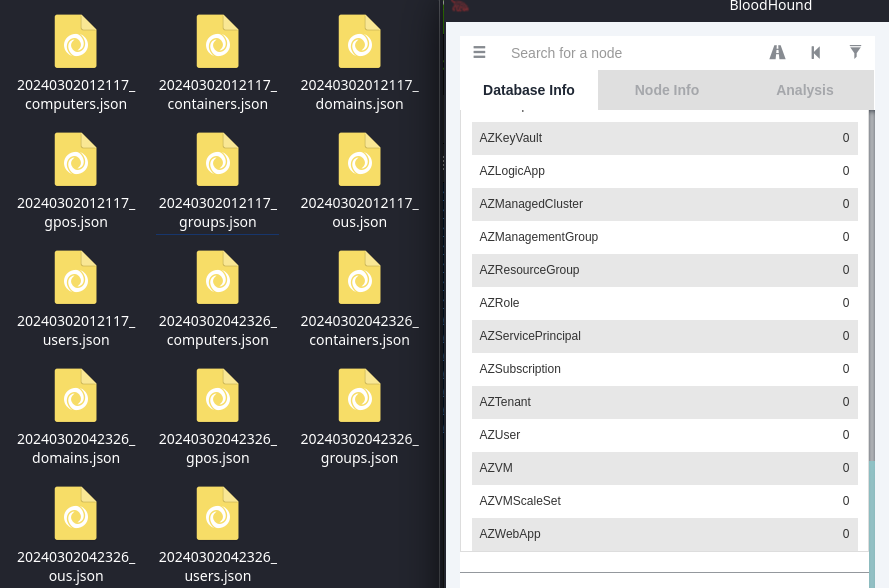
Drag and drop these files in to Bloodhound for analysis